1. http.HandleFunc
http.HandleFunc는 함수입니다.- 특정 경로에 대해 요청을 처리할 핸들러를 등록합니다.
- 등록된 함수는
func(http.ResponseWriter, *http.Request)시그니처를 따릅니다.
1-1. 사용 예제
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"net/http"
)
type Response struct {
Message string `json:"message"`
}
func helloHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json") // 응답 헤더 설정
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK) // 헤더에 Status코드 설정
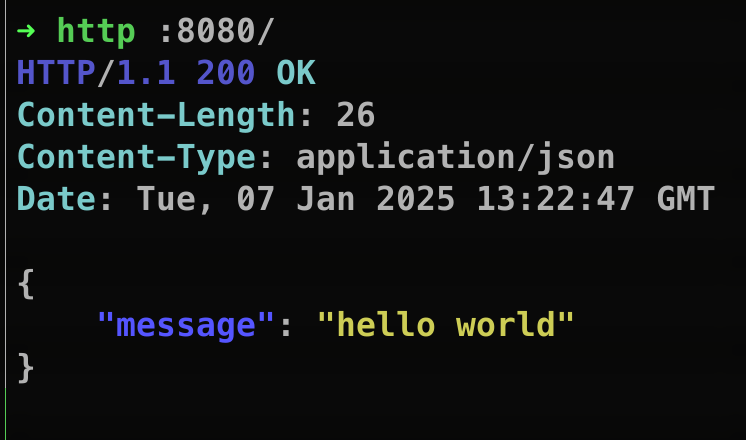
response := Response {
Message: "hello world",
}
if err := json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(response); err != nil {
fmt.Errorf("failed to encode json reponse", err)
}
}
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/", helloHandler) // '/' 경로에 핸들러 등록
fmt.Println("Server start on port :8080")
if err := http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil); err != nil {
panic("failed to start server")
}
}
2. http.HandlerFunc
http.HandlerFunc는 타입입니다.http.Handler인터페이스를 구현하는 함수 타입으로 정의됩니다.- 이 타입은
ServeHTTP메소드를 통해http.Handler로 동작할 수 있습니다.
2-1. 사용 예제
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"net/http"
)
type Response struct {
Message string `json:"message"`
}
func helloHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json") // 응답 헤더 설정
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK) // 헤더에 Status코드 설정
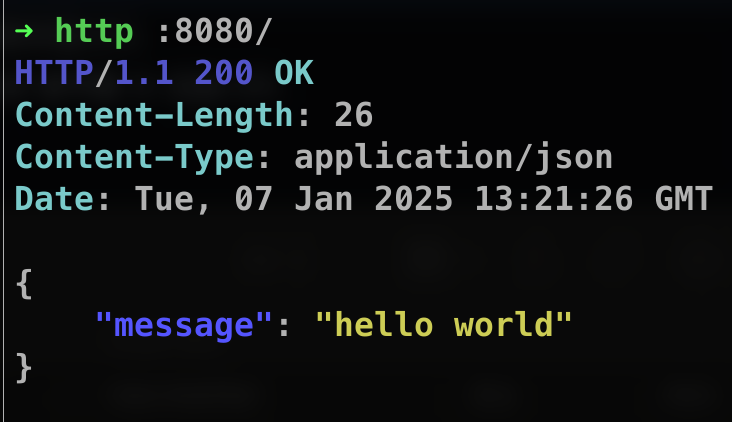
response := Response {
Message: "hello world",
}
if err := json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(response); err != nil {
fmt.Errorf("failed to encode json reponse", err)
}
}
func main() {
handler := http.HandlerFunc(helloHandler) // 함수 -> 핸들러 변환
http.Handle("/", handler) // 핸들러 등록
fmt.Println("Server start on port :8080")
if err := http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil); err != nil {
panic("failed to start server")
}
}
3. 차이점
1-1과 2-1은 정확히 같은 결과를 볼 수 있습니다. 타입과 함수의 차이라는것은 알겠는데 사용할 때 어떻게 다르고 언제 어떤걸 사용해야 할까요?
우선 http.handlerFunc는 함수를 http.Handler로 변환시킵니다. 그렇기에 핸들러가 명시적으로 필요하거나 미들웨어를 사용시 사용할 수 있습니다.
3-1. 미들웨어 예제
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"net/http"
)
type Response struct {
Message string `json:"message"`
}
// 로깅 미들웨어
func loggingMiddleware(next http.Handler) http.Handler {
return http.HandlerFunc(func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Printf("Request: %s %s\n", r.Method, r.URL.Path) // 로그 출력
next.ServeHTTP(w, r) // 다음 핸들러 호출
})
}
// 기본 핸들러
func helloHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json") // 응답 헤더 설정
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK) // 헤더에 Status코드 설정
response := Response {
Message: "hello Middleware",
}
if err := json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(response); err != nil {
fmt.Errorf("failed to encode json reponse", err)
}
}
func main() {
// 기본 핸들러를 미들웨어로 감쌈
http.Handle("/", loggingMiddleware(http.HandlerFunc(helloHandler)))
fmt.Println("server start on port :8080")
if err := http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil); err != nil {
panic("failed to start server")
}
}
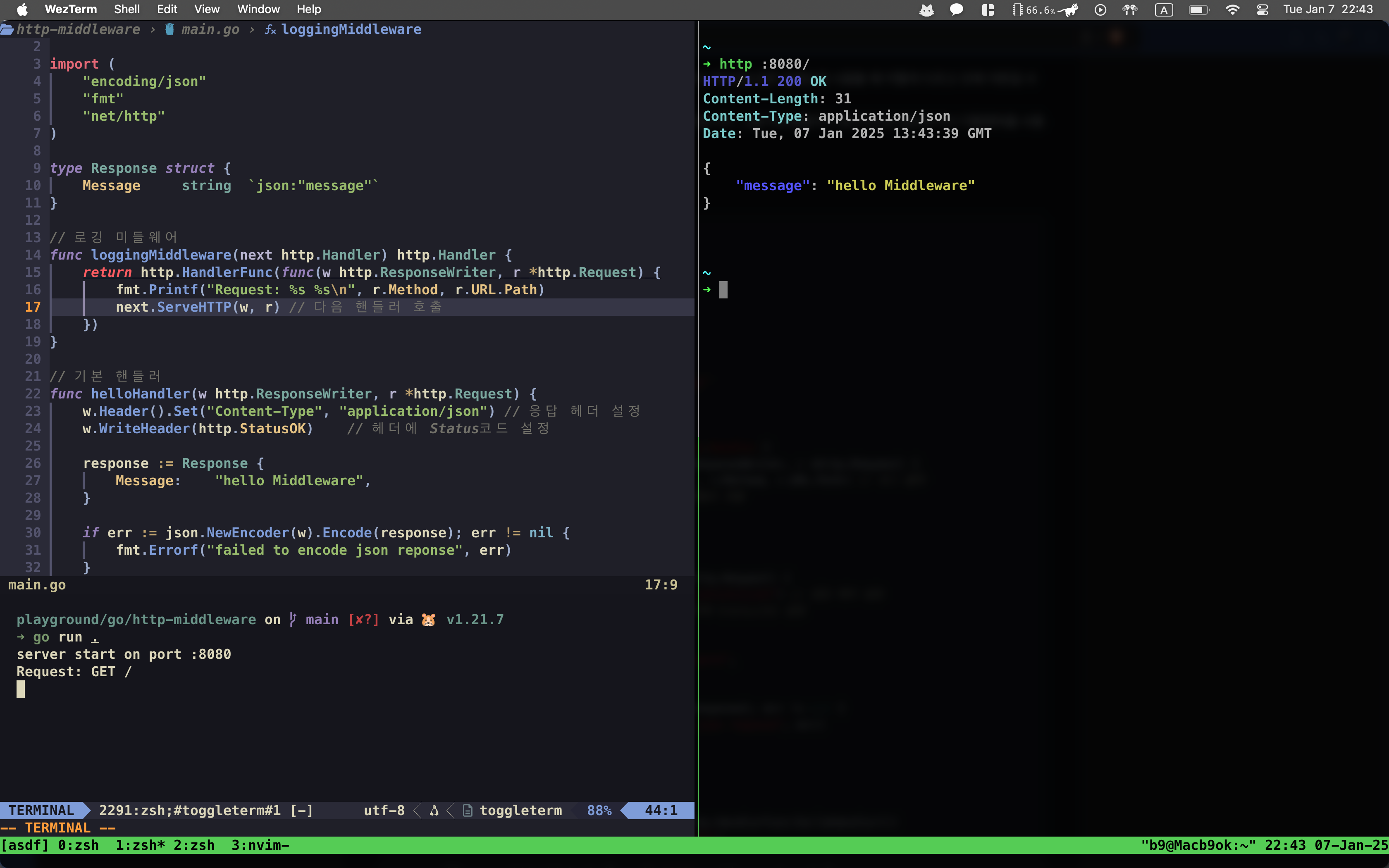
왼쪽화면아래의 터미널을 보면
미들웨어가 작동하여 :8080/로 접근하자 r.Method와 r.URL.Path를 출력합니다
logginMiddleware()에서 Handler를 인자로 받는 이유는, handler.ServeHTTP()가 Handler인터페이스에 정의되어있기 때문입니다.
type Handler interface {
ServeHTTP(ResponseWriter, *Request)
}
4. 차이점 정리
| 특성 | http.HandlerFunc | http.HandleFunc |
|---|---|---|
| 역할 | 타입 (함수를 http.Handler로 변환) | 함수 (라우트와 핸들러를 연결) |
| 사용 목적 | 핸들러로 사용하거나 미들웨어로 연결 | 특정 경로에 핸들러를 간단히 등록 |
| 내부 동작 | ServeHTTP 메서드를 통해 요청 처리 | 내부적으로 HandlerFunc로 변환 |
| 사용 방법 | 직접 핸들러로 사용 | 경로와 핸들러 함수를 연결 |
| 사용 예시 | http.Handle("/path", HandlerFunc) | http.HandleFunc("/path", handlerFunc) |
4. 마무리
최근 Go를 사용해서 이것저것 시도해보고 있습니다.
회사에서 필요한 스크립트 등도 일부러 Go로 짜보고 이전 토이프로젝트도 Go로 포팅해보는등..
상당히 매력적인 언어임이 분명한것 같습니다.
읽어주셔서 감사합니다.
>> Home